Methods are an essential part of Java programming. They are used to group a set of statements together to perform a specific task, which can be called whenever needed. In this tutorial, we will discuss the different types of methods in Java, including predefined methods and user-defined methods, and their advantages. We will also cover how to call methods with and without parameters, and the basics of memory allocation for methods calls.
Additionally, we will explore the concept of recursive methods, which allow a method to call itself repeatedly until a specific condition is met. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a good understanding of the various aspects of methods in Java and how to use them effectively in your programs.
What is a Method in Java?
A method is a block of code that performs a specific task and can be called from other parts of the program. It encapsulates a set of instructions that performs a well-defined function, and helps to organize the program’s code into reusable and modular units. In Java, methods are defined inside classes, and can be called by other methods or from outside the class using the class object.
Syntax of Methods in Java
The syntax of a method in Java consists of several components:
access_modifier return_type method_name(parameter_list) {
// method body
}
- access_modifier: This specifies the visibility of the method, which can be public, private, or protected. The access modifier determines which parts of the program can access the method. If the method is public, it can be accessed from anywhere in the program; if it’s private, it can only be accessed from within the same class; and if it’s protected, it can be accessed from within the same class or any subclass.
- return_type: This specifies the type of value that the method returns. It can be a primitive data type such as int, double, or boolean, or a reference type such as String or Object. If the method doesn’t return anything, its return type is void.
- method_name: This is the name of the method, which can be any valid identifier in Java. It should be chosen to reflect the function of the method, so that it’s easy to understand and use.
- parameter_list: This is a comma-separated list of input parameters that the method accepts. Each parameter has a data type and a name, which are used to pass values into the method. The parameter list is enclosed in parentheses and can be empty if the method doesn’t require any input parameters.
- method body: This is the code that performs the specific task of the method. It’s enclosed in curly braces and consists of a set of statements that define the method’s functionality.
Method Declaration
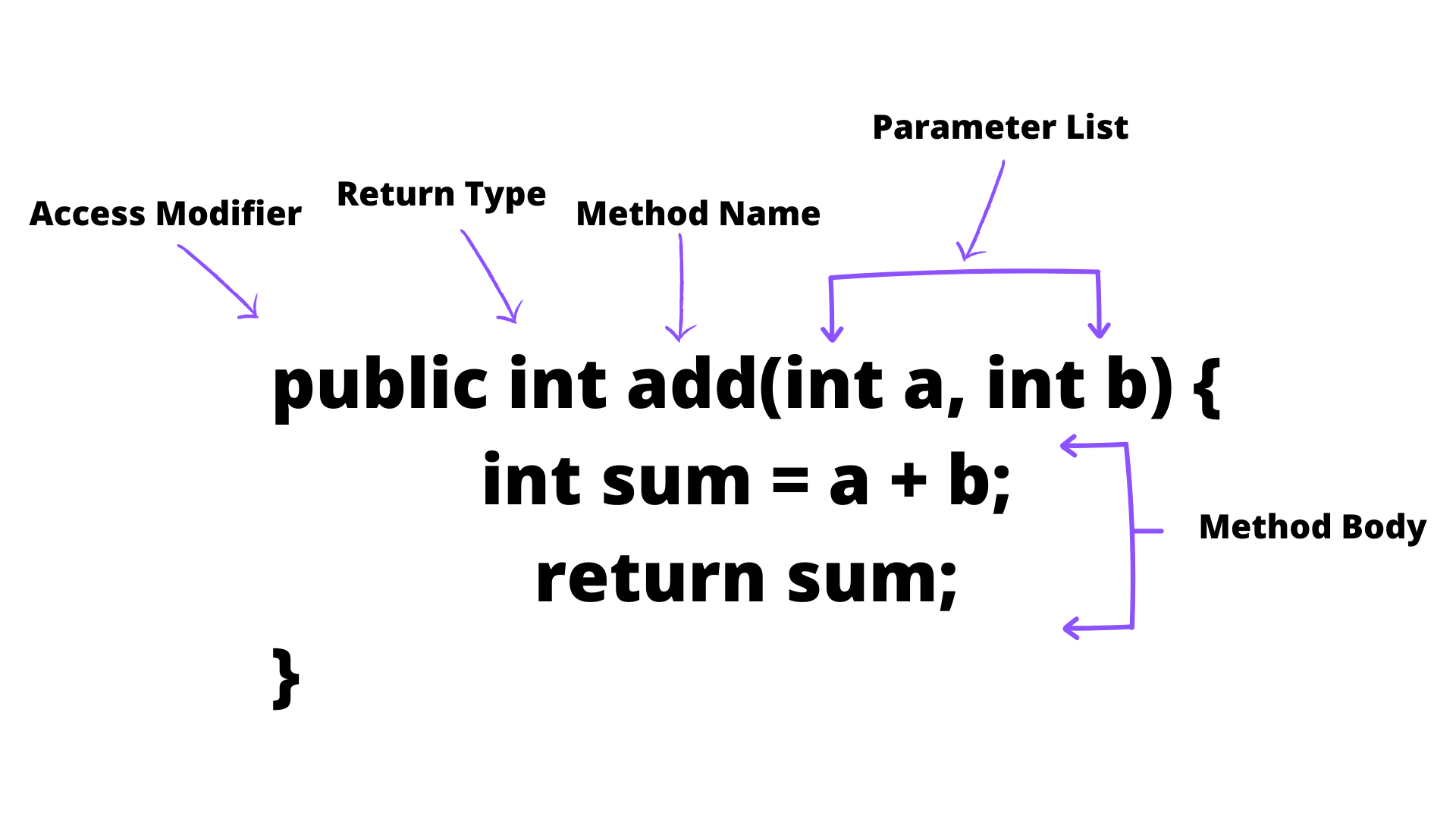
To declare a method in Java, you must provide the method signature and the method body. The method signature consists of the method name and parameter list, and optionally the return type. Here’s an example of a method that takes two integers as input and returns their sum:
public int add(int a, int b) {
int sum = a + b;
return sum;
}
In this example, the method name is add, the parameter list is (int a, int b), and the return type is int. The method body calculates the sum of the two input integers and returns the result using the return statement.
What is a Method Signature?
The method signature is a combination of the method name and the parameter list, without the return type. It’s used to uniquely identify a method within a class, and to distinguish it from other methods with the same name but different parameters or return types. For example, the method signature of the add method above is add(int a, int b).
How to Name a Method?
Naming a method is an important aspect of writing readable and maintainable code in Java. Here are some best practices for naming a method:
- Use a descriptive name: A method name should accurately describe what the method does, using clear and concise language. Avoid using abbreviations or acronyms that might not be clear to other developers.
- Use a verb-noun pair: A common convention in Java is to use a verb-noun pair for method names. The verb describes the action performed by the method, while the noun describes the object the method operates on. For example, “calculateTotal” or “sortArray”.
- Use camelCase: In Java, it’s common to use camelCase for naming methods. This means that the first word of the name is lowercase, while subsequent words are capitalized. For example, “calculateTotal” or “sortArray”.
- Follow the Java naming conventions: Java has established naming conventions for methods, which help to make the code more readable and consistent. These conventions include using camelCase, starting the name with a verb, and using descriptive names. For example, “getFirstName” or “setLastName”.
- Avoid generic names: Avoid using generic names like “doSomething” or “processData”, which don’t provide any useful information about what the method actually does. Use specific names that accurately describe the method’s function.
- Be consistent: It’s important to be consistent in your naming conventions across your codebase. This helps to make the code more readable and easier to maintain. If you’re working on a project with other developers, it’s a good idea to establish naming conventions and stick to them.
By following these best practices, you can create method names that are descriptive, clear, and consistent with Java conventions. This will help to make your code more readable and maintainable, which is especially important for large and complex projects.
What are the Advantages of Using Methods?
There are several advantages to using methods in Java:
- Modularity: By breaking down a program into smaller methods, it becomes easier to manage and maintain. Each method encapsulates a well-defined function and can be tested and debugged independently of other methods. This makes it easier to find and fix bugs, and to modify or extend the program’s functionality without affecting other parts of the code.
- Reusability: Methods can be called from multiple parts of a program, making them versatile and reusable. This reduces code duplication and makes the program more efficient and maintainable.
- Abstraction: Methods can hide the details of the implementation from other parts of the program, allowing the user to interact with a simplified interface. This improves the readability and maintainability of the code, as well as reducing the complexity and potential for errors.
- Code organization: By using methods to encapsulate related functions, the program’s code can be organized into logical units, making it easier to understand and navigate. This is particularly useful for large programs or programs with complex functionality.
- Code readability: Methods with descriptive names and well-defined input and output parameters can make the program’s code more readable and easier to understand. This is particularly important for collaborative projects where multiple developers may be working on the same codebase.
Overall, using methods in Java can help to make the code more modular, reusable, maintainable, and understandable. It’s a best practice to use methods whenever possible, and to keep them simple, well-organized, and well-documented.
Calling Methods in Java
In Java, a method is called by using its name, followed by parentheses. The parentheses can be empty or contain one or more arguments, depending on the method’s signature.
Calling a Method Without Parameters
To call a method without parameters, you simply write the method name followed by parentheses. For example, let’s create a method called printHelloWorld that prints “Hello, World!” to the console:
public class Example {
public static void printHelloWorld() {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}
To call this method, we would write:
Example.printHelloWorld();
This will execute the printHelloWorld method, which will print “Hello, World!” to the console.
It’s important to note that the printHelloWorld method is defined as public static, meaning it can be called from anywhere and does not require an instance of the Example class to be created.
Calling a Method With Parameters
To call a method with parameters, you need to pass in values that match the types and order of the parameters in the method’s signature. For example, let’s create a method called sum that takes two integers as parameters and returns their sum:
public class Example {
public static int sum(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}
To call this method with the values 3 and 5, we would write:
int result = Example.sum(3, 5);
This will execute the sum method with the values 3 and 5, and store the result in the result variable.
It’s important to ensure that the values passed in match the types and order of the parameters in the method’s signature. Otherwise, the method will not execute correctly and may produce errors.
In summary, calling a method in Java involves writing the method name followed by parentheses, and passing in values if the method has parameters. By following the method’s signature and passing in the correct values, you can execute the method and obtain its result.
Types of Methods in Java
In Java, methods are the building blocks of a program. They are used to group a set of statements together to perform a specific task. Methods can be classified into two categories: user-defined methods and predefined methods.
User-Defined Methods
User-defined methods are created by the programmer to perform specific tasks. These methods can be created in any class and can be called from anywhere in the program, provided they are accessible. User-defined methods can have any number of parameters and can return any type of value or no value at all.
Here’s an example of a user-defined method that takes two integers as input and returns their sum:
public class Example {
public static int sum(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
}
In this example, the sum method is defined as public static, meaning it can be called from anywhere and does not require an instance of the Example class to be created. The method takes two integers as input and returns their sum.
When defining a user-defined method, the method signature must be specified. The method signature consists of the method name and its parameters. The return type is not considered part of the signature.
Here’s an example of a user-defined method with multiple parameters and a void return type:
public class Example {
public static void printSum(int a, int b) {
int sum = a + b;
System.out.println("The sum of " + a + " and " + b + " is " + sum);
}
}
In this example, the printSum method takes two integers as input and does not return a value. Instead, it prints the sum of the two integers to the console.
Predefined Methods in Java
Predefined methods, also known as built-in or standard library methods, are provided by Java or third-party libraries for common operations. These methods are already defined and can be called by the programmer to perform specific tasks. Some examples of predefined methods in Java include:
System.out.println(): prints text to the consoleMath.sqrt(): calculates the square root of a numberString.toLowerCase(): converts a string to lowercase
Here’s an example of how to use the System.out.println() method to print text to the console:
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
This will output the text “Hello, World!” to the console.
Predefined methods can be called directly without being defined in the program. However, it’s important to understand their functionality and how to use them properly.
Standard Library Methods Examples
The Java standard library provides a wide range of predefined methods for various tasks. Here are a few examples of standard library methods in Java and how they can be used:
Example 1: Using the Math.sqrt() method to calculate the square root of a number
double num = 25; double squareRoot = Math.sqrt(num); System.out.println(squareRoot);
Output:
5.0
We declare a double variable num and assign it a value of 25. We then use the Math.sqrt() method to calculate the square root of num and assign it to the double variable squareRoot. Finally, we print out the value of squareRoot using System.out.println().
Example 2: Using the String.toLowerCase() method to convert a string to lowercase
String name = "JOHN"; String lowerCaseName = name.toLowerCase(); System.out.println(lowerCaseName);
Output:
john
We declare a String variable name and assign it the value "JOHN". Next we use the toLowerCase() method to convert name to lowercase and assign the result to the String variable lowerCaseName. As a result, we print out the value of lowerCaseName using System.out.println().
Example 3: Using the Arrays.sort() method to sort an array of integers
int[] numbers = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5};
Arrays.sort(numbers);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
Output:
[1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 9]
We declare an array of integers numbers and assign it a series of values. Afterward we use the Arrays.sort() method to sort the elements in numbers in ascending order. Lastly, we print out the sorted numbers array using Arrays.toString().
Memory Allocation for Methods Calls
When a method is called in Java, memory is allocated to store the method’s parameters, local variables, and any other necessary data. The memory is allocated on the call stack, which is a portion of memory reserved for storing method calls and their associated data.
Every time a method is called, a new frame is added to the top of the call stack to store the method’s data. When the method completes execution, the frame is removed from the stack and the memory is released. This means that the amount of memory used by a program can fluctuate as methods are called and completed.
Let’s take a look at an example to better understand how memory allocation works for method calls in Java:
public class MemoryAllocationExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
int sum = addNumbers(a, b);
System.out.println(sum);
}
public static int addNumbers(int x, int y) {
int result = x + y;
return result;
}
}
In this example, the main method is called and memory is allocated for its parameters (args) and local variables (a, b, and sum). The addNumbers method is then called and memory is allocated for its parameters (x and y) and local variables (result). Once the addNumbers method completes execution, its frame is removed from the call stack and the memory used by the method is released.
It’s important to note that if a method calls another method, the memory for the called method is allocated on top of the calling method’s frame. This creates a “stack” of frames, with the most recently called method on top.
In conclusion, understanding memory allocation for method calls in Java is important for writing efficient and effective programs. By understanding how memory is allocated and released, you can optimize your code and avoid memory leaks.
Bonus: Recursive Methods
Recursive methods are methods that call themselves during their execution. A recursive method consists of two parts: the base case and the recursive case. The base case is the condition under which the method stops calling itself, while the recursive case is the condition under which the method calls itself.
Recursive methods can be used to solve problems that can be broken down into smaller, simpler problems of the same type. For example, computing the factorial of a number can be solved using a recursive method.
Let’s take a look at an example of a recursive method that computes the factorial of a number:
public static int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return n * factorial(n-1);
}
}
In this example, the factorial() method takes an integer n as its argument and returns the factorial of n. The base case is when n is equal to 0, in which case the method returns 1. The recursive case is when n is greater than 0, in which case the method calls itself with the argument n-1 and multiplies the result by n.
Let’s say we call factorial(4). The method will call itself with the argument 3, then with the argument 2, then with the argument 1, and finally with the argument 0. At this point, the base case is reached and the method returns 1. The method then returns the result of the previous call multiplied by n, which is 1 * 1 * 2 * 3 * 4, which equals 24.
One thing to keep in mind when using recursive methods is that they can consume a lot of memory, especially if the recursion depth is large. Each call to the method creates a new stack frame, which takes up memory. If there are too many stack frames, the program may run out of memory and crash. Therefore, it is important to carefully design recursive methods to ensure that they don’t consume too much memory.
In conclusion, recursive methods can be a powerful tool for solving problems that can be broken down into smaller, simpler problems of the same type. However, they should be used with caution, as they can consume a lot of memory if not designed carefully. You can learn about recursion in Java through this tutorial What is Recursion in Java?
Conclusion
In conclusion, methods are an essential feature of Java programming that allows for modular, organized, and reusable code. By understanding the syntax, types, and advantages of methods, you can become a more efficient and effective Java programmer.
We have covered various aspects of methods in Java, including how to create and call them, the different types, and memory allocation for method calls. Additionally, we briefly covered recursive methods as a bonus topic. To further your knowledge of Java programming, make sure to visit the Java Tutorials for Beginners page for more related topics.